Composites testing laboratory - research equipment
Leco ONH836 Elemental Analyzer
Optima 4300DV ICP-OES, optical emission spectrometer
Perkin Elmer Optima 8300 DV ICP optical emission spectrometer
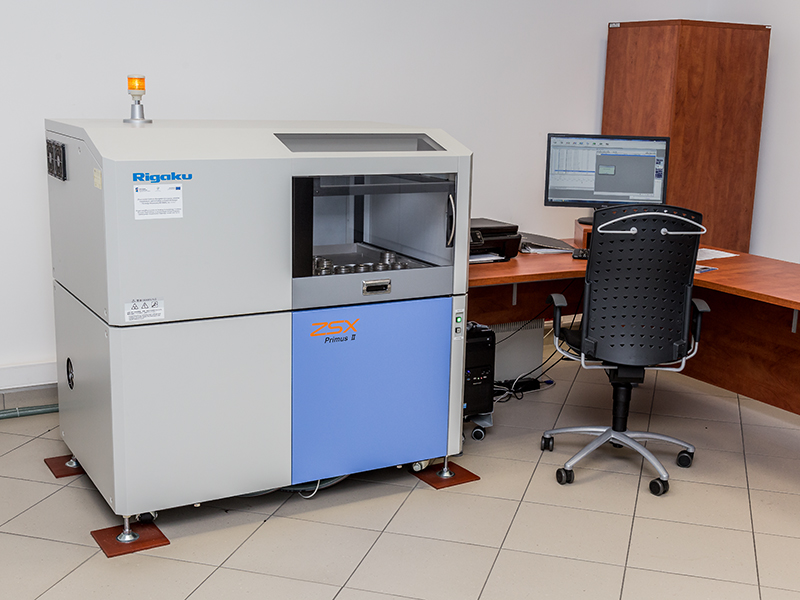
Rigaku ZSX Primus II, WDXRF spectrometer
- Analyzes the elemental composition of samples of metals and alloys, sediments, dusts, ashes and the content of elements in composites, plastics, rubbers as well as petroleum products and car catalysts
-
The 4kW x-ray tube allows for very precise analytical measurements
-
Allows to test surfaces of heterogeneous composition
-
Enables mapping of the distribution of elements present on the surface of samples and filters
-
Allows you to test the content of elements in engine and transmission oils, cooling fluids, lubricants, etc.
-
Wide analytical scope
Agilent 1260 Infinity High Performance Liquid Chromatograph with Diode Array Detector
- Used in the qualitative and quantitative analysis of soluble compounds in the mobile phase
- It enables the analysis of compounds with different molecular weights, volatility and high temperature unstable compounds
- It is used in the analysis of carbonyl compounds (including formaldehyde and acetaldehyde) and phthalates emitted from materials
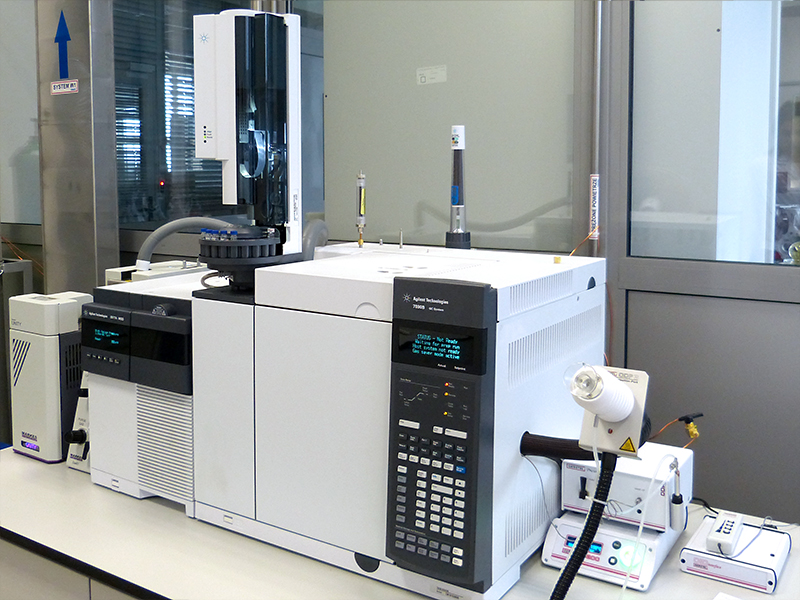
Agilent 7820A gas chromatograph equipped with Agilent 7693A liquid sample loader and FID flame ionization detector
Agilent 7890A gas chromatograph
- MSD Agilent 5975C Inert mass spectrometer and FID flame ionization detector
- Agilent 7683B liquid sample loader
- Headspace Sampler Agilent G1888
- Termodesorber Markes UNITY2 with ULTRA2 sample changer
- Microcell for emission tests
- Headspace - e.g. testing of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) emissions under static conditions
- Temperature desorption - e.g. testing of VOC emissions based on air samples collected on appropriate adsorbent beds
- VOC emission tests from materials under dynamic conditions (e.g. according to VDA 278)
- Direct feeding of liquid samples
Agilent 7890B gas chromatograph
- MSD Agilent 5977A mass spectrometer and NPD nitrogen phosphor detector
- Gertsel olfactometric port
- Agilent 7683B liquid sample loader
- termodesorber Markes UNITY2
- Identification of compounds
- Analysis of the quantitative composition of the samples
- Odor analysis of individual compounds separated during chromatographic analysis, with simultaneous identification using mass spectrometry
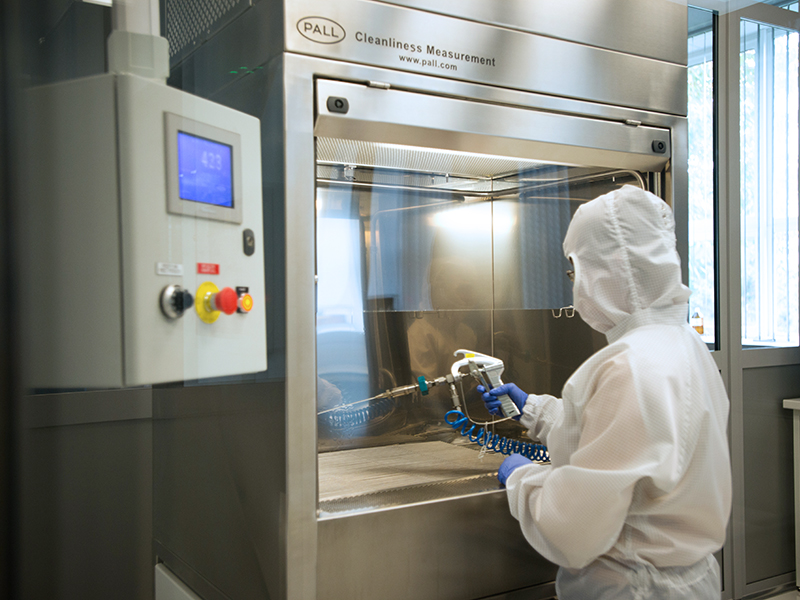
Clean Room - a room for cleanliness testing, with PALL Cleanliness Cabinet stand for spray washing of tested parts
- ISO 6 clean room
- It is equipped with PALL Cleanliness Cabinet - an automated spray washing cabin, with replaceable nozzles and adjustable flow, allowing for testing the cleanliness of objects with a complex shape
- Depending on the size and shape of the tested objects, impurities from their surfaces may also be emitted in an ultrasonic bath
- Possibility of using various techniques for washing contaminants from objects: spray washing, ultrasound extraction, rinsing or shaking
- The equipment of the room allows for gravimetric analysis of pollutants
- Separated contamination of objects can also be subjected to a quantitative analysis (size, amount and type of contamination: metallic, non-metallic particles and fibers) based on dedicated optical microscopes
- Using the scanning electron microscope (SEM-EDX) it is possible to analyze the elemental composition, based on it also hardness, dirt particles
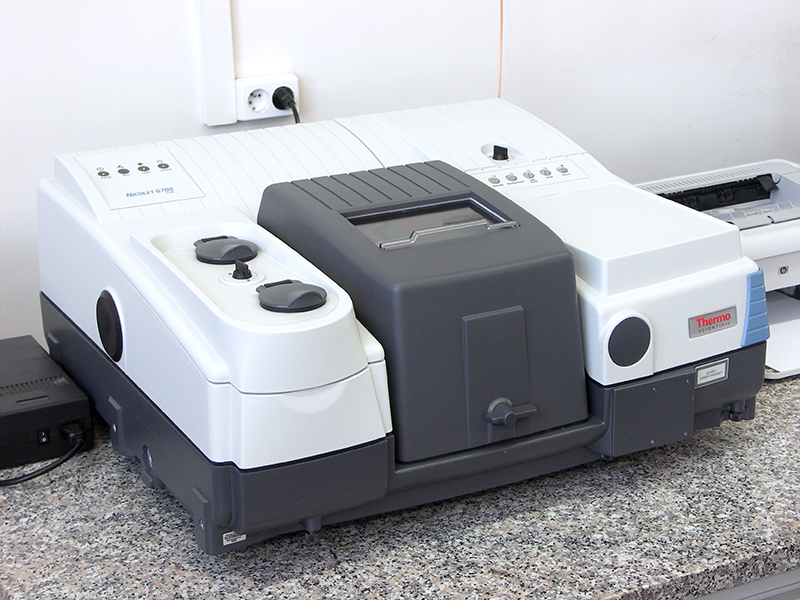
FTIR Thermo Scientific NICOLET 6700 infrared spectrometer
- It is used to identify the base material of plastics, foams, adhesives, rubbers, solvents, petroleum products
- Allows for the identification of small sizes of solid impurities (very often in a non-destructive way)
- Enables the performance of comparative analyzes to determine the differences between the sample base materials
- Allows for the analysis of surface contamination in the form of stains, discoloration, tarnish by direct collection or extraction with a properly selected solvent
- Enables quantitative measurements - benzene content, FAME content, glycol content, soot content, degree of oxidation and nitration
- In specific cases, it also allows the identification of inorganic substances, e.g. fillers
FTIR ThermoFisher Scientific NICOLET is50 infrared spectrometer
- It is used to identify the base material of plastics, foams, adhesives, rubbers, solvents, petroleum products
- Allows for the identification of small sizes of solid impurities (very often in a non-destructive way)
- Enables the performance of comparative analyzes to determine the differences between the sample base materials
- Allows for the analysis of surface contamination in the form of stains, discoloration, tarnish by direct collection or extraction with a properly selected solvent
- In specific cases, it also allows the identification of inorganic substances, e.g. fillers
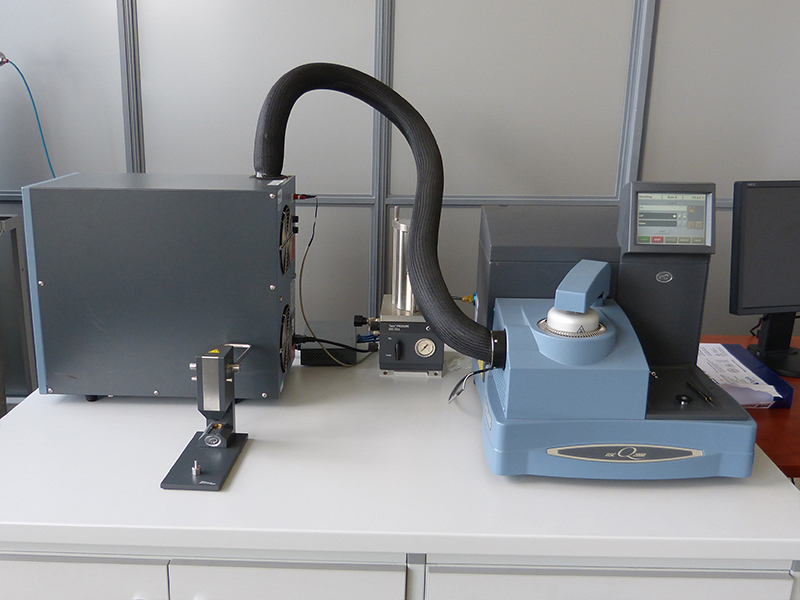
TA Instruments Q2000 Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
TA Instruments Q500 thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) coupled with a Nicolet iS50 FTIR spectrometer
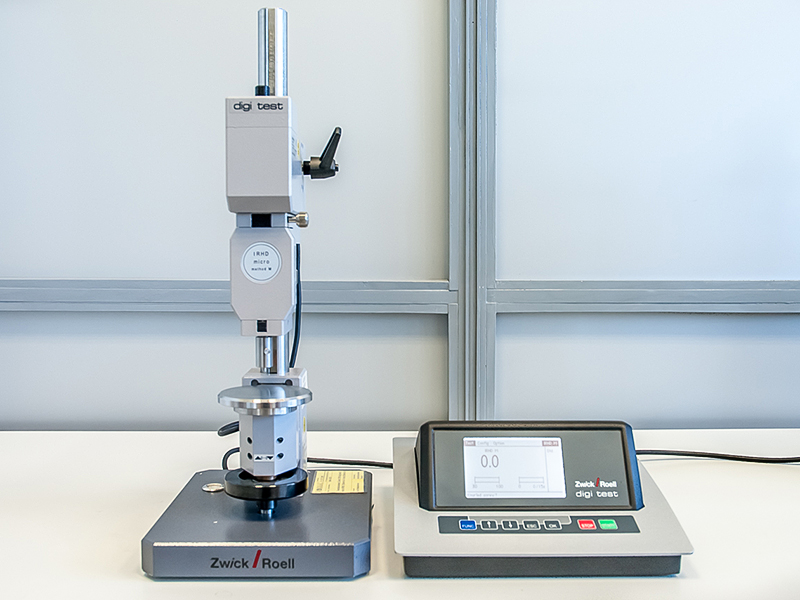
Zwick / Roell 3105 digi test hardness tester
Hardness of metals and metal alloys
- Brinell in the range of 1-3000 kg (ball, 1; 2.5; 5 and 10 mm)
- Rockwell (HRA, HRB, HRC, HRD, HRE, HRF, HRG, HRH, HRK, HR15N)
- Knoopa HK1
- Vickers (HV0.3 - HV100)
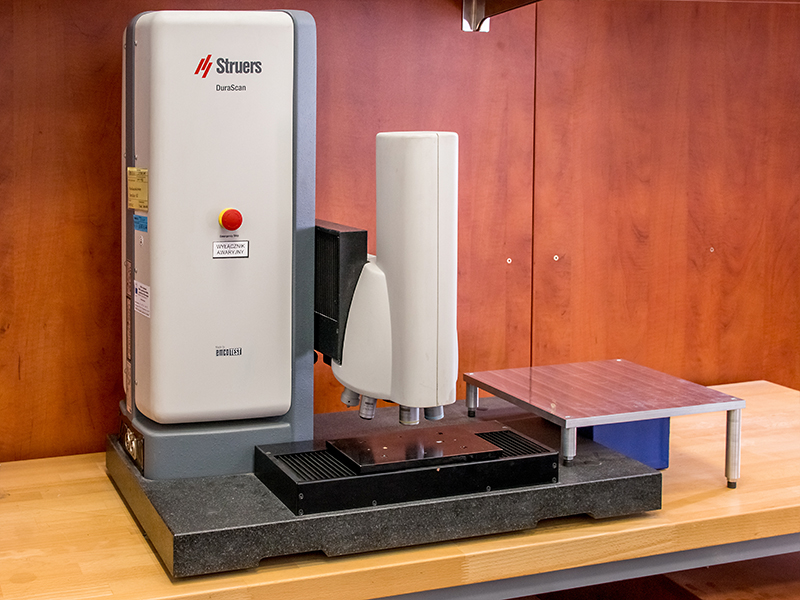
- EMCOTEST - DuraScan - 50 micro hardness tester (pictured)
- Universal hardness tester Zwick / Roell ZHU-250
- Brinell DHB-3000 WPM Heckert hardness tester
- Rockwell hardness tester HRC - HM-1810 - WPM Heckert
- Brinell DHB-3000 Hautec hardness tester
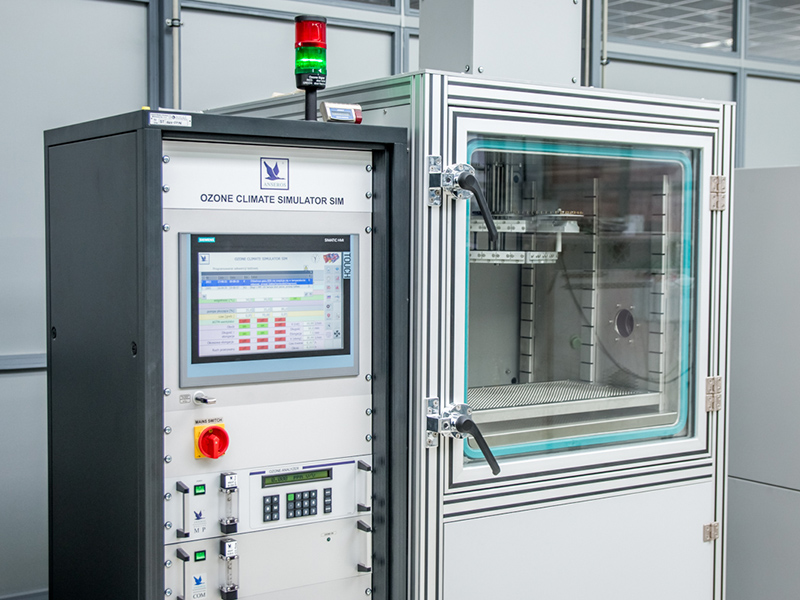
Ozone resistance test chamber ANSEROS SIM6300-TH
Atlas Xenon Weather-Ometer Accelerated Aging Test Chamber Ci 3000 + and Ci 4000 Series
- Radiation intensity in W / m2 and light energy in MJ / m2
- Black thermometer temperature and chamber air temperature, ranging from 40° to 120°C
- Regulation of relative air humidity in the range from 10 to 100% RH
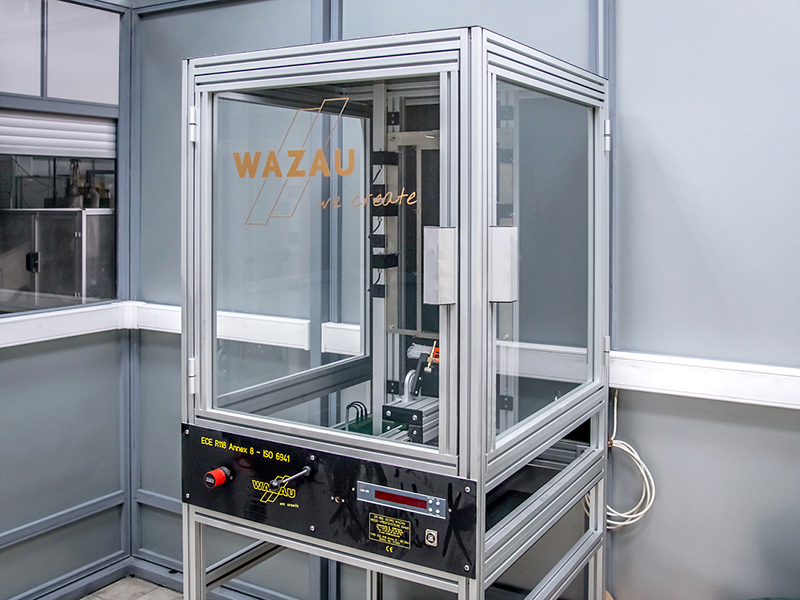
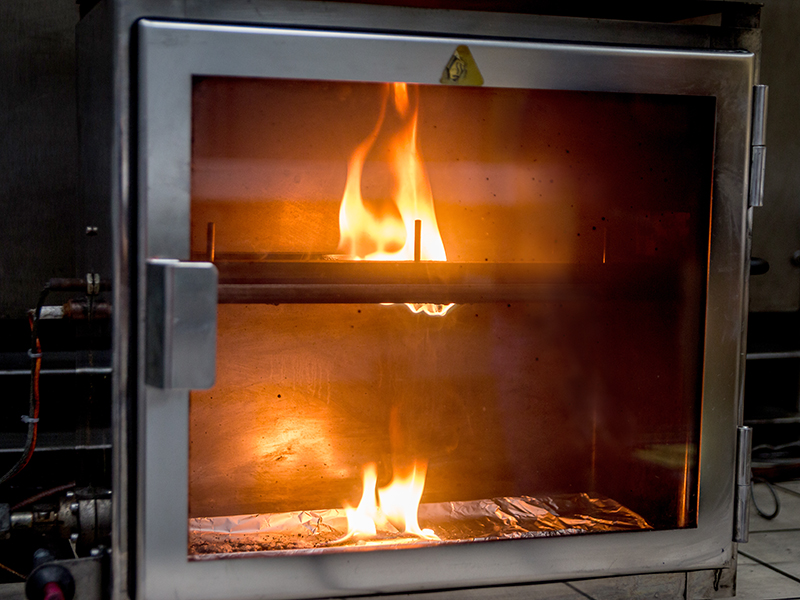
WAZAU Vertical Flammability Test Chamber
WAZAU Horizontal Flammability Test Chamber
- PN-ISO 3795
- UNECE Regulation No. 118 Series 02 Rev.2 / Add.117 / Rev.1 / Amend.1
- DIN 75200
- FMVSS 302
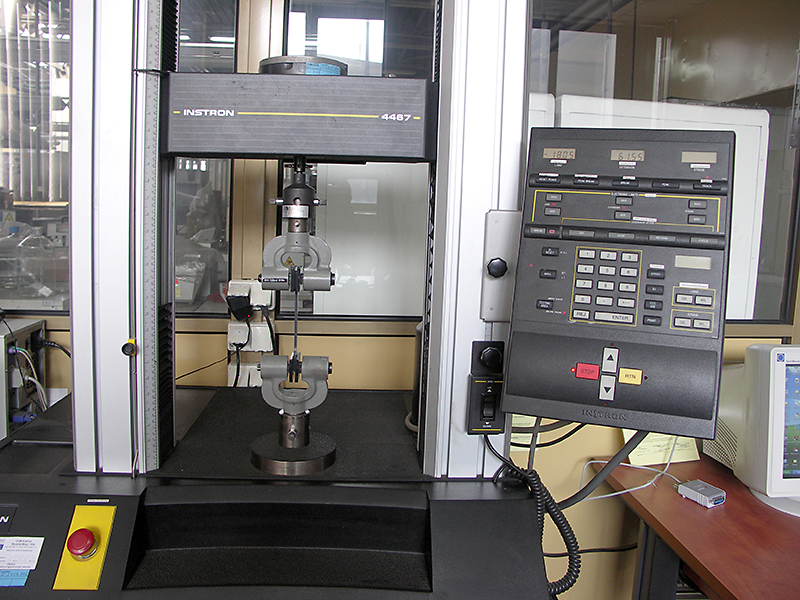
Instron 4467 testing machine
- Equipped with measuring heads: up to 500 N and up to 30 kN and an extensometer
- Possibility of testing at a temperature from -70 ° C to 250 ° C
- Allowing to determine, among others: tensile strength, tear strength, permanent deformation after compression, hysteresis under compressive stress, strength at static bending, modulus of elasticity in bending
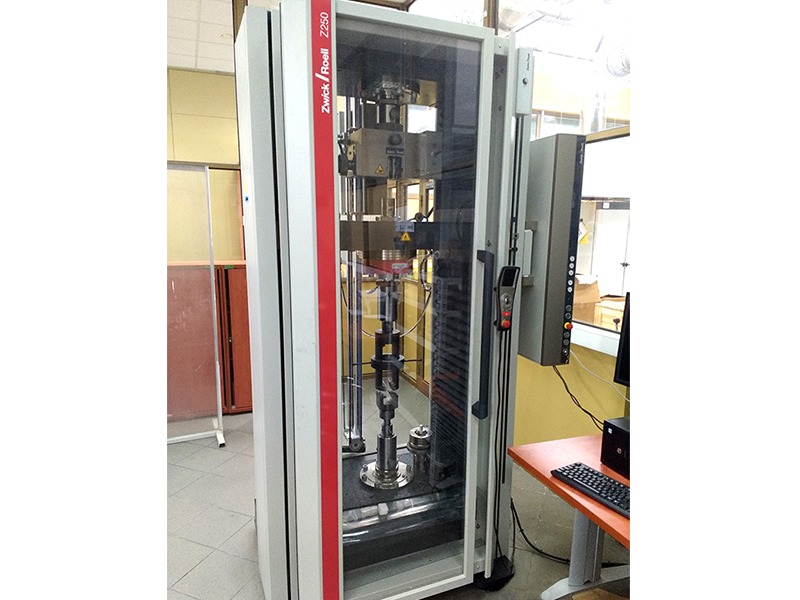
Zwick testing machine 250 kN Allround floor
- Strength Rm
- Yield strength Re
- The yield point Rp
- Elongation A
- Contraction Z
- PN-EN ISO 898-1, without 9.13
- PN-EN ISO 898-5, without 9.4
- PN-EN 28839
- PN-EN ISO 6157-2
- PN-EN ISO 898-2
- PN-EN ISO 2320
- Flattening method according to PN-EN ISO 8492
- Expansion method according to PN-EN ISO 8493
Apparatus for the determination of water by the Karl Fischer method
Odor testing laboratory
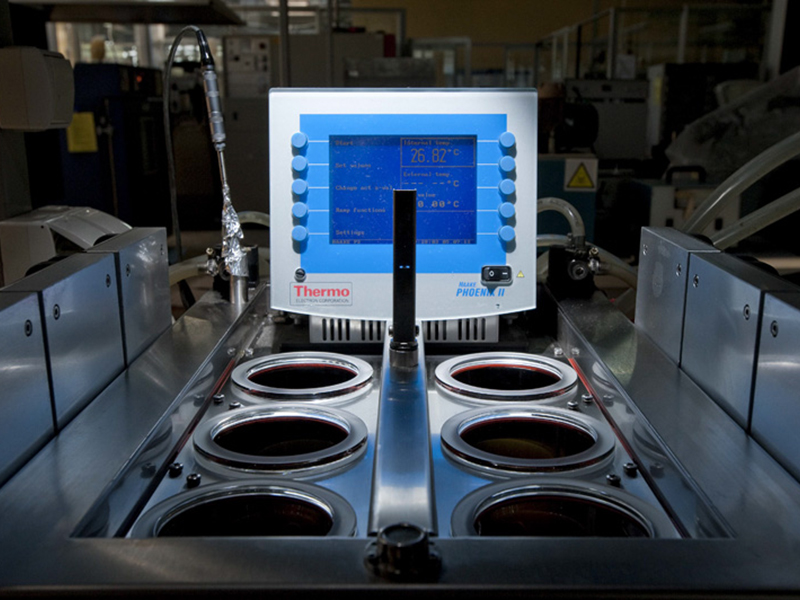
Product fogging (Fogging Tester HAAKE PHOENIX II + K20 with DC30)
- Haze value - the quotient of the gloss value (reflectometer, 60 °) of a glass plate with deposited volatile substances and the gloss value of the same clean glass plate
- Haze value - the quotient of the transmittance of a glass plate with deposited volatile substances and the transmittance of the same clean glass plate
- Condensation of components (G) - the difference in mass between the aluminum foil with deposited volatile substances and the mass of the foil before the test
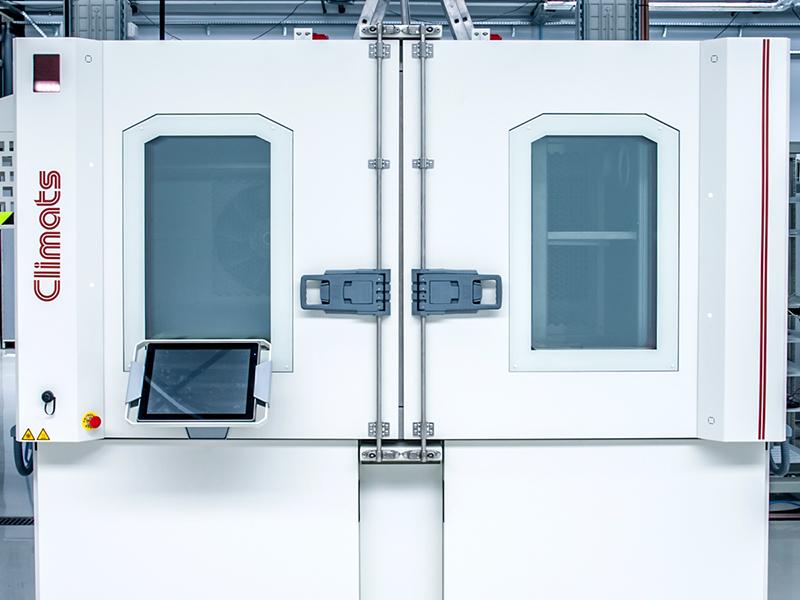
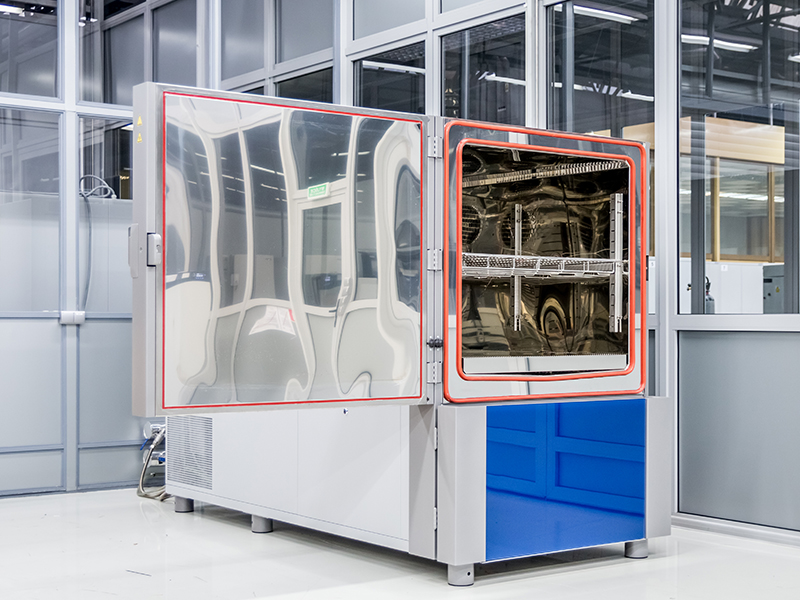
Climats shock chamber
- Temperature range: -70 to 180 ° C
- Direction of basket movement: horizontal
- Basket capacity: 512 l
- Basket dimensions: (80x80x80) cm
- Max. basket load: 80 kg
- Max. adjustable transition time: 10… 40 s
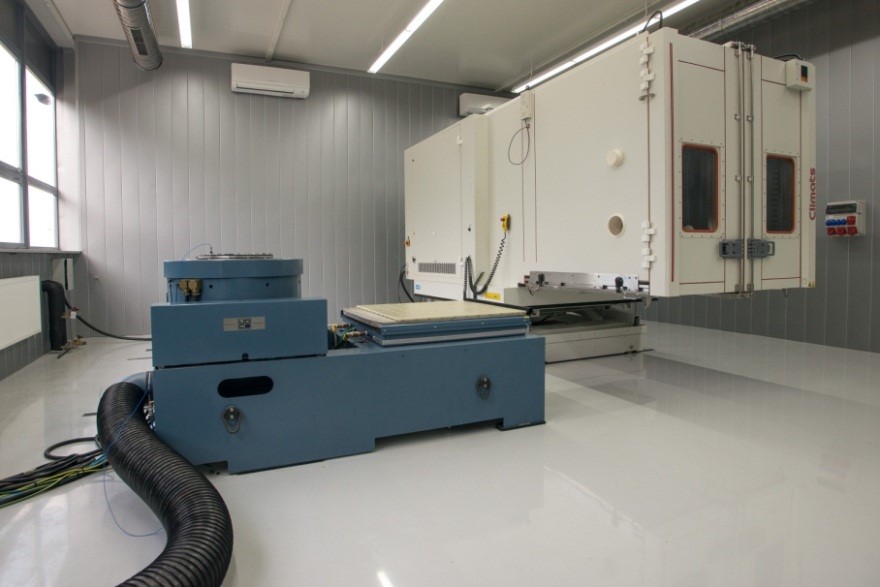
Vibration system cooperating with the Climats climatic chamber
- Force: 35.6 kN
- Frequency range: 4 to 3000 Hz
- Maximum displacement: 76 mm
- 100 g maximum acceleration (sinus / random); 260 g (mechanical shocks)
- Maximum load: 600 kg
- Table dimensions: 600 x 600 mm - vertical; 914 x 914 mm - horizontal.
- Interior dimensions: 1500 x 1500 x 1500 mm (volume 3.4 m3),
- Temperature range (work with a vibrating stand): from -40 to 160 ° C; when working alone: from -75 to 180 ° C,
- Relative humidity: 10 to 98% (at a temperature of +10 to 90 ° C),
- Temperature change rate: 10 ° C / min (with internal heat dissipation).
Climatic and temperature chambers
Salt-humidity and salt-climate chambers
Kesternich chamber
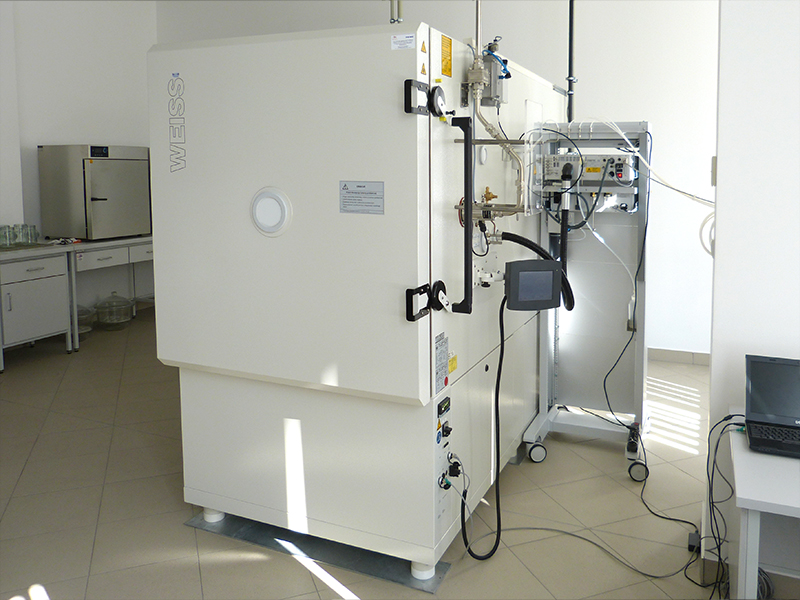
Weiss WKE1000 chamber
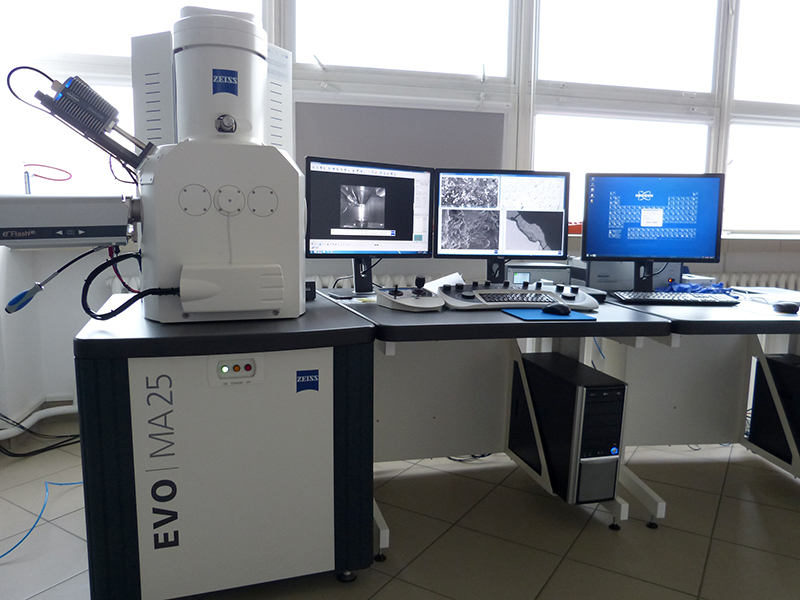
Scanning electron microscope SEM EVO MA25 with EDS and EBSD analyzers by Bruker
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis and mapping the elemental composition of samplesEvaluation of the fracture surface fractography enabling the determination of the fracture nature, material discontinuities and e.g. hydrogen embrittlement, identification of undesirable inclusions on the fracture surface
- Analysis of the size and type of non-metallic inclusions
- Linear microanalysis of diffusion coatings and layers
- Classification of pollutants on filters - technical cleanliness tests
- Possibility of testing relatively large samples (300x200x200 mm)
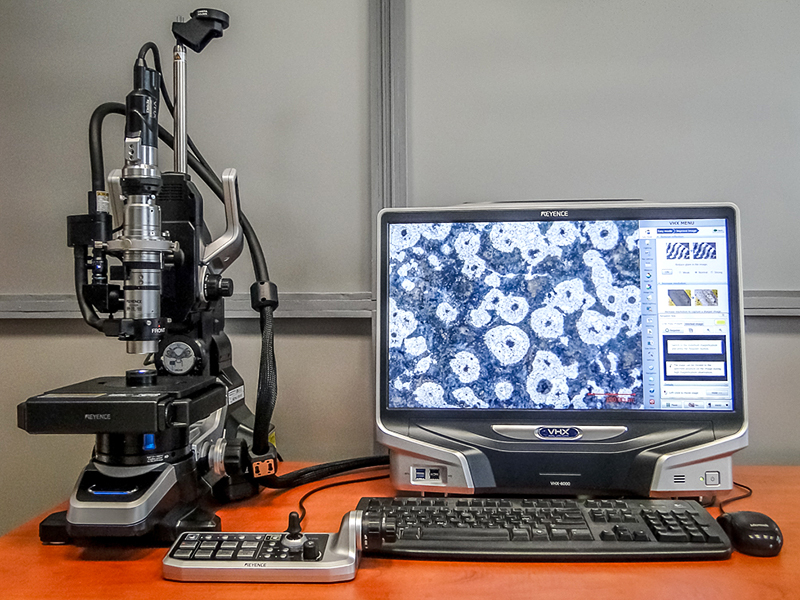
Keyence VHX-6000 digital microscope
- Magnification 20 - 1000x
- Advanced image sharpening
- High quality and resolution images
- Observation in reflected and transmitted light
- Observation at varying angles
- Removing reflections
- A high-speed automated table that allows you to scan the surface
- Quick folding of the surface (up to 4 cm)
- 3D surface visualization
- Surface roughness measurement
- Automatic particle counting
- Automatic edge detection
- Real-time measurements
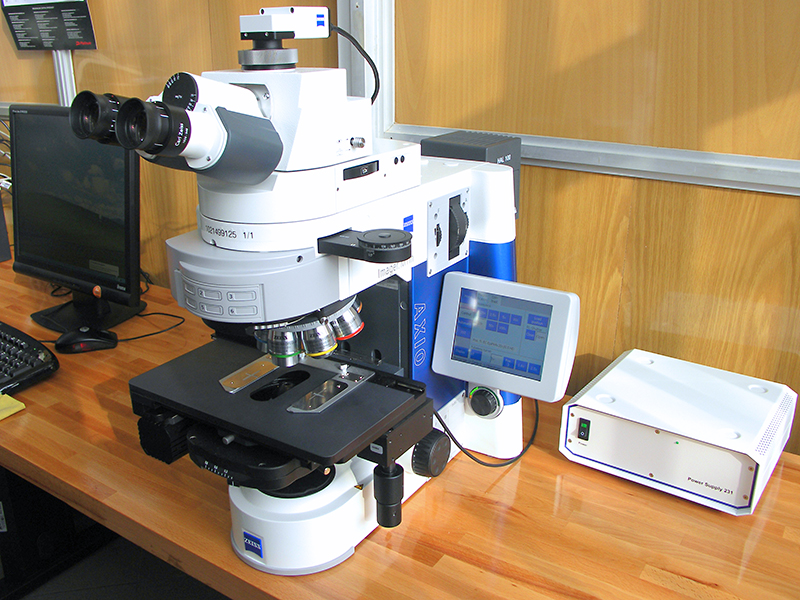
Zeiss M1m metallographic microscope
- Magnification 12.5 - 2500x.
- Reflected light observation techniques:
- Bright field
- Dark field
- Polarization
- Differential interference contrast.
- Differential interference contrast in circular polarization.
- The possibility of observation in transmitted light.
- Built-in automated table that allows you to scan the surface.
- Module for folding surfaces - Mosaix (up to 4 cm).
- 3D module.
- Particle Analysis module for filter contamination analysis
- NMI module for the analysis of non-metallic inclusions
- Module for graphite analysis in cast irons
- Grain size analysis module
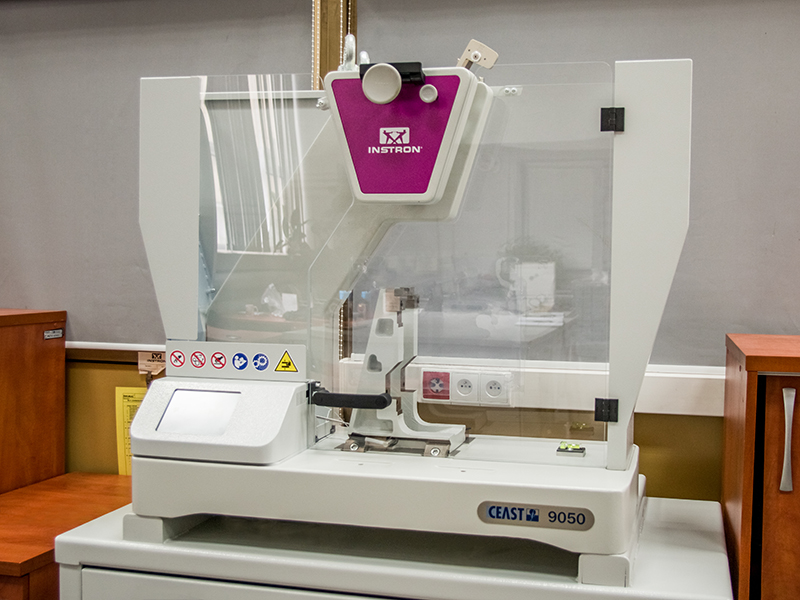
Instron Hammer - CEAST 9050
Charpy's method
The Izod method
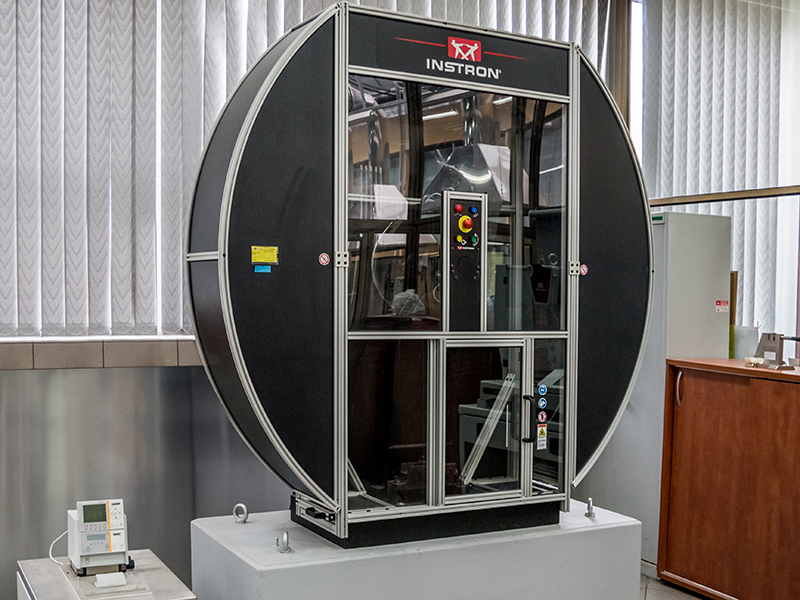
Swing Hammer - Instron 450MP
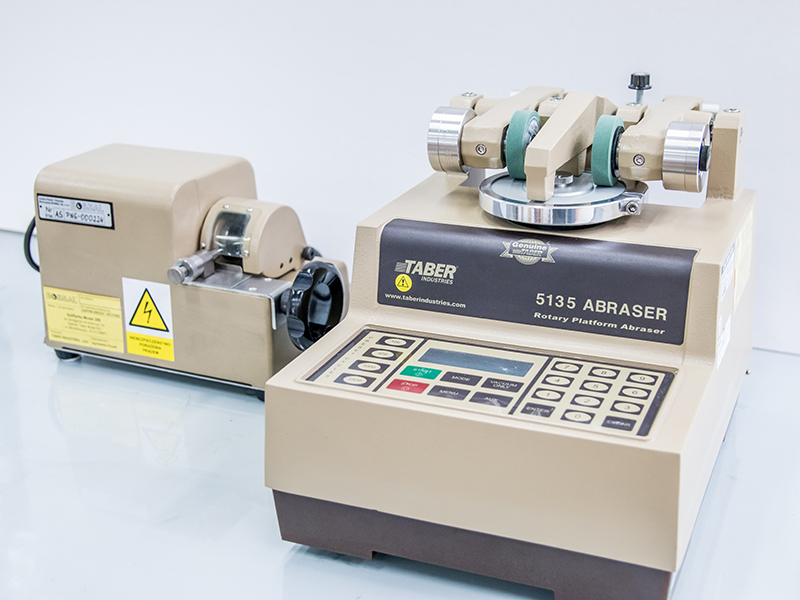
Rotary abrasion tester - TABER Abraser - Model 5135
It is a device designed for accelerated material wear tests. The test consists in mounting a flat sample on a movable platform, which rotates around its axis at a given speed. Two abrasive discs are lowered onto the surface of the test sample and pressed with appropriate force. The wheels turn in opposite directions and make a full circle on the surface of the sample. This system allows the abrasion resistance of the material to be tested in every direction, regardless of the structure, weave or grain pattern in the material.
- ISO 15082
- ISO 7784-2
- ISO 5470-1
- ISO 10074
- SAE J365
- DIN 53754
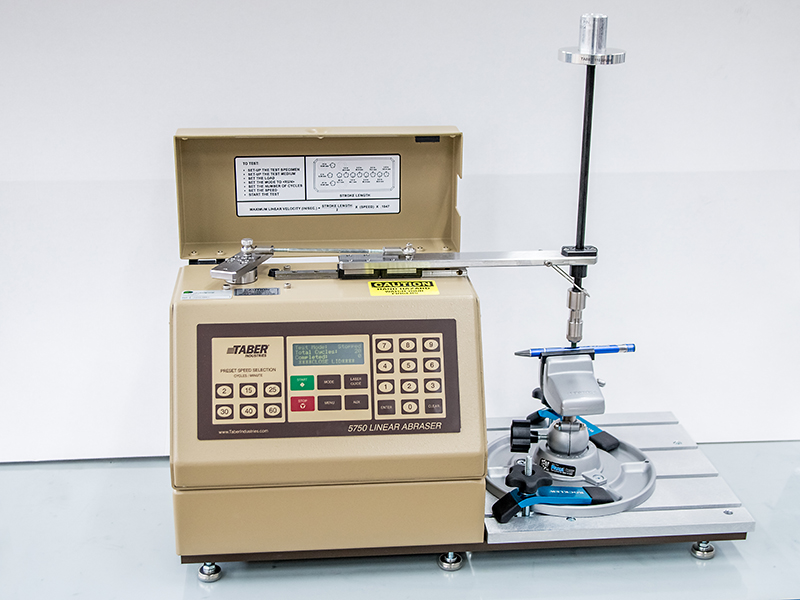
TABER Linear Abraser - Model 5750
The apparatus is designed to test the resistance of materials and products to surface abrasion and to assess the relative strength or susceptibility of the material surface to physical damage such as wear and abrasion, scratching, gouging, scratching, abrasion, color transfer (usually called color fastness) and others.
The linear abrasion tester can be used for both dry and wet tests. It is designed to test samples of virtually any size and shape.
- ISO 105-X12
- PV 3906
- D42 1775
- AA-0134